Mouth breathing in children
- Lotus Dental
- Apr 1, 2020
- 3 min read
Mouth breathing: The adverse effects on facial growth, health, learning and behaviour

Few parents realize how malleable the facial bones of a six-year-old child are and how quickly habits such as leaving the mouth open or thumb-sucking can spoil a child’s appearance for ever.
It is difficult for a lay person to know if the face of a young child is growing correctly, because most young children look ‘cute’. However, mouth breathing and poor tongue posture can result in a long face with a narrow upper jaw and crowded teeth.
The upper jaw stops growing in most boys and girls before the age of 10. Hence early treatment is the key.
It is important to not just straighten teeth with braces but also to ensure correct tongue posture and nasal breathing before the orthodontic treatment is completed.
One of the main causes of relapse of orthodontic treatment is when the main cause of malocclusion (incorrect tongue posture or mouth breathing) is not treated, and only the teeth are straightened.
Causes and symptoms of mouth breathing
One of the main causes of mouth breathing in children is allergies and blocked noses caused by enlarged adenoids and tonsils.
Here is an image of a young boy with normal breathing and a balanced facial profile to begin with, until he was introduced to an allergen (possibly the family cat). This led him to breathe through his mouth and end up with a long face, with crowded upper and lower jaws.
The following are some of the symptoms that may be experienced by a child who is not breathing correctly or has sleep apnoea:
Dark translucent areas under eyes
Behavioural problems
Inability to focus in class
Bed wetting after the age of 6 yrs
Feeling tired and easily falling asleep during the day
Snoring , teeth grinding and night sweats
Mouth breathing is associated with high blood pressure and cardiac failures
Nasal respiration is responsible for the production of nitric oxide. This nitric oxide, inhaled via the nasal respiration, is known to increase oxygen exchange efficiency and increase blood oxygen by 18% while improving the lung’s ability to absorb oxygen. Nitric oxide is also a strong vasodilator and brain transmitter that increases oxygen transport throughout the body and is vital to all body organs including smooth muscles of the heart and blood vessels.
The negative impact of sleep disordered breathing in children’s growth and development is well documented
These children are often well below their peers in terms of height and weight. Sleep apnoea is on the rise in both adults and children.
A child with sleep apnoea may often get misdiagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Mouth breathing often irritates the mucosa and often causes the tonsils and adenoids to enlarge. These may need to be removed surgically when they obstruct the airway and negatively affect sleep.
Treatment options for children with a crowded mouth and narrow jaws
Treatment normally involves a jaw expansion device and associated treatments to address tongue, breathing and body alignment issues.
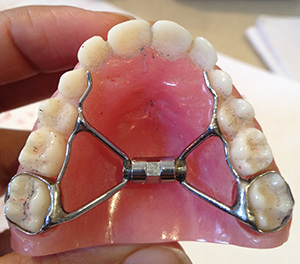
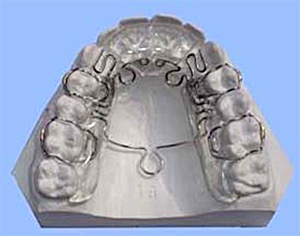
Jaw expansion appliances
These can be removable or fixed. The appliances include the ALF appliance, Schwartz plate, and the hirax and myofunctional appliances.
A slow expansion achieved over 6-9 months is ideal. Rapid expansion is also occasionally done, using fixed appliances.
Jaw expansion appliances
These can be removable or fixed. The appliances include the ALF appliance, Schwartz plate, and the hirax and myofunctional appliances.
A slow expansion achieved over 6-9 months is ideal. Rapid expansion is also occasionally done, using fixed appliances.
Associated treatments
Most patients with a narrow jaw need help with an Oral Mycologist/Respiratory physiotherapist to retrain the tongue to sit up on the palate instead of being on the lower teeth.
Patients who are mouth breathers need breathing retraining, and in that process their posture and head posture improves.
Occasionally some patients may need orthotics by a podiatrist to correct the overall posture, helping to keep the oral expansion stable.
In cases where the adenoids and tonsils are excessively enlarged and blocking the airway an Ear Nose and Throat specialist may be required.









Comments